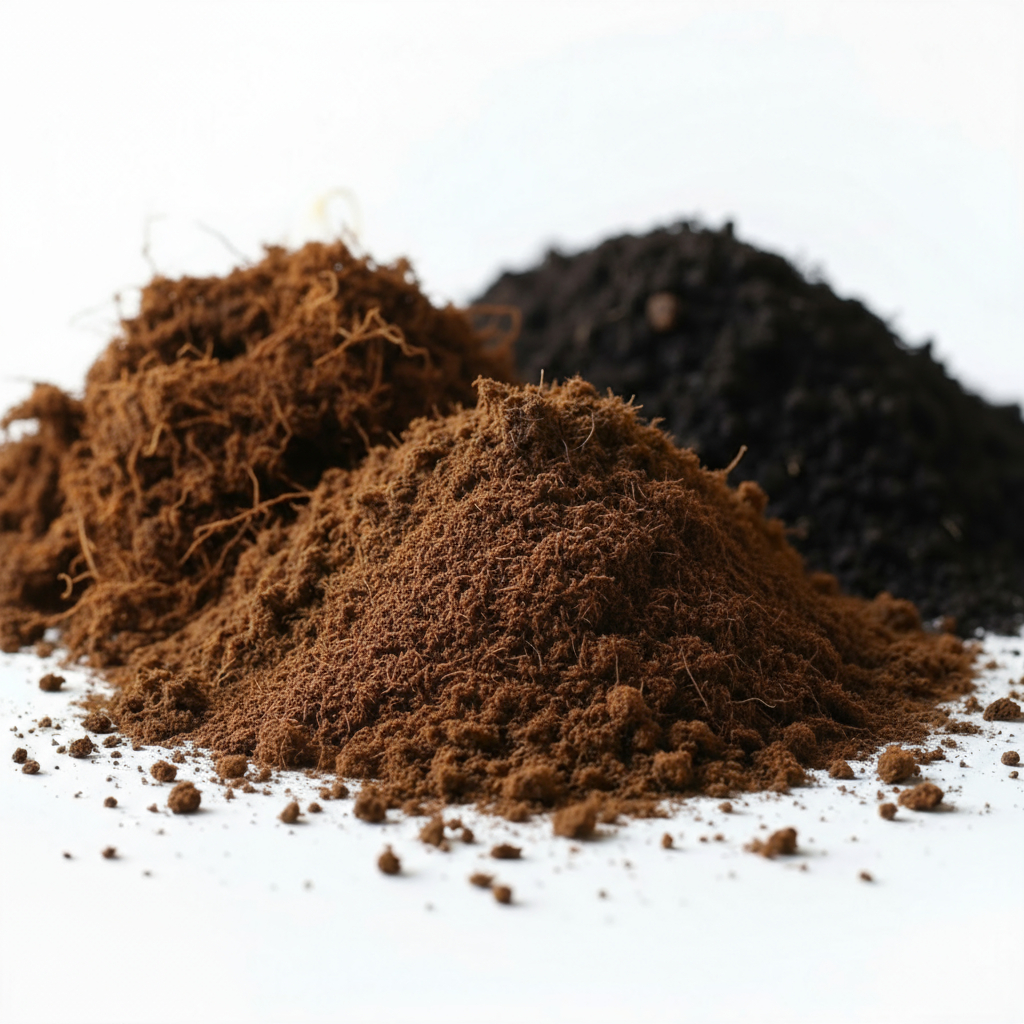

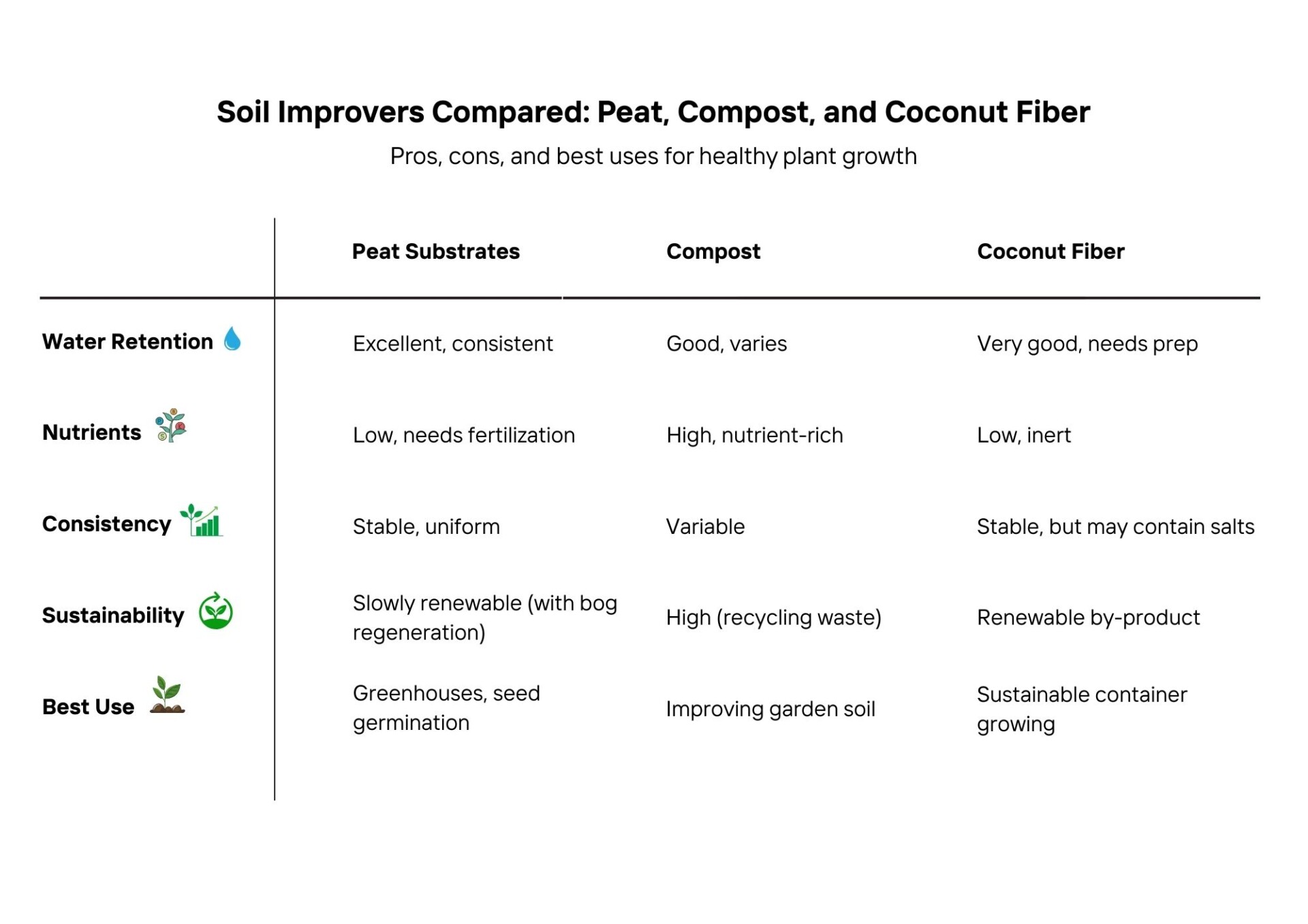
Gardeners and growers often wonder which soil improver works best. Should you choose peat substrates, compost, or coconut fiber? Each has unique benefits — from water retention to sustainability — and knowing the differences helps you make the right decision for your plants.
Peat provides consistency, compost enriches the soil with nutrients, and coconut fiber is a renewable alternative. The best option depends on your growing method, plant type, and environmental priorities.
Read on to see how these three popular soil improvers compare.
Peat Substrates: Reliable and Consistent

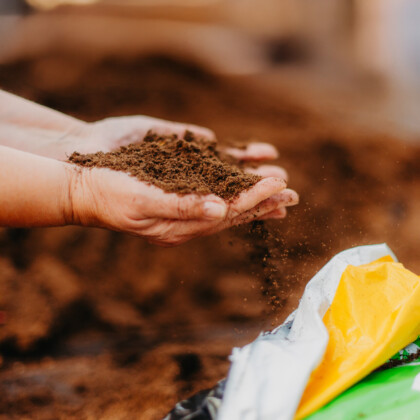
Peat substrates are widely used in horticulture because of their stable structure and predictable results. They are especially valued in professional greenhouses, seed germination, and nursery production.
Advantages of peat:
- High water-holding capacity for better moisture control;
- Good aeration that supports strong root development;
- Adjustable and stable pH values;
- Free from weeds and most pathogens;
- Long shelf life and consistent quality.
Disadvantages:
- Low in natural nutrients, requiring added fertilization;
- Sustainability concerns, though bog regeneration practices are improving.
👉 Explore our peat substrates to learn how ETEPEK ensures quality and reliability in every batch.
Compost: Nutrient-Rich and Sustainable

Compost is an organic amendment made from decomposed plant and food waste. It’s a go-to solution for gardeners who want to improve soil fertility naturally.
Advantages of compost:
- Rich in organic matter and essential nutrients;
- Improves microbial activity and soil structure;
- Recycles organic waste into a useful soil improver.
Disadvantages:
- Quality can vary depending on how it’s produced;
- Risk of weed seeds or pathogens if not fully decomposed;
- Shorter storage time and heavier handling compared to peat.
For more guidance on composting standards, see the European Compost Network.
You can also learn more about Peat Moss Bedding Repurposing Into Compost.
Coconut Fiber (Coir): Renewable Alternative

Coconut fiber, or coir, is made from coconut husks and has grown in popularity as an alternative to peat moss.
Advantages of coconut fiber:
- Renewable and eco-friendly by-product;
- Excellent aeration and drainage;
- Resistant to decomposition, offering long-lasting structure.
Disadvantages:
- Can contain salts, so washing is often necessary before use;
- Lower buffering capacity than peat;
- May be more expensive or harder to source in some regions.
Peat vs Compost vs Coconut Fiber: Direct Comparison
Peat vs Compost
- Peat: stable, uniform, and ideal for controlled horticulture.
- Compost: nutrient-rich, but variable in quality.
Peat vs Coconut Fiber
- Peat: offers better buffering capacity and consistency.
- Coconut fiber: sustainable, but may require extra preparation.
Compost vs Coconut Fiber
- Compost: feeds the soil with nutrients.
- Coconut fiber: provides structure and drainage without nutrients.
👉 ETEPEK offers premium peat substrates trusted by growers worldwide.
Which Soil Improver Should You Choose?
Well, it really depends on what you’re growing and how you want to grow it. Here’s a quick cheat sheet:
-
Seedlings & greenhouse crops → Go with peat for its consistency and water retention.
-
Garden beds & soil enrichment → Compost wins for fertility and soil health.
-
Eco-friendly container gardening → Choose coconut fiber for sustainability and structure.
Pro tip: Many growers mix two or even all three! For example:
-
50% peat + 30% compost + 20% coir makes a well-balanced mix for containers.
-
Compost + coir is a great organic option for raised beds.
Bonus Tip: Peat Isn’t Just for Plants. Did you know? Peat also makes excellent bedding for livestock and poultry due to its absorbency and odor control. See ETEPEK’s animal bedding products for your animal care needs.
Conclusion
No single soil improver is perfect for every situation. Peat substrates deliver consistency, compost adds fertility, and coconut fiber offers sustainability. Many growers combine them to achieve a balance between performance, soil health, and environmental responsibility.
Key Takeaways
Peat substrates ensure reliable results, aeration and moisture control.
Compost enriches soil with nutrients and organic matter.
Coconut fiber is renewable and provides aeration and structure.
The best choice depends on plant type, growing method, and sustainability goals.


